Recommendation for individuals using a screenreader: please set your punctuation settings to "most."
Descriptive Statements:
- Demonstrate knowledge of the structure and function of different macromolecules (i.e., lipids, proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids), cell theory, and the characteristics of living organisms.
- Apply knowledge of the structure and function of organelles in various types of cells (e.g., eukaryotic, prokaryotic, plant, animal).
- Analyze how organisms obtain, use, and store matter and energy, including through processes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
- Demonstrate knowledge of cell division processes (i.e., mitosis, meiosis, and binary fission) and their role in reproduction, growth development, and the life cycles of living organisms.
- Apply knowledge of the structures and functions of plants and their role in the processes and feedback systems used to maintain life (e.g., homeostasis, metabolism), including the levels of biological organization.
- Apply knowledge of the structures and functions of animals, excluding humans, and their role in the processes and feedback systems used to maintain life (e.g., homeostasis, metabolism), including the levels of biological organization.
- Apply knowledge of the structures and functions of humans and their role in the processes and feedback systems used to maintain life (e.g., homeostasis, metabolism), including the levels of biological organization.
- Apply knowledge of the functions of specialized structures in plant systems and animal behavior used as strategies to increase the probability of successful reproduction.
- Demonstrate knowledge of scientific practices (e.g., asking questions; developing and using models; planning and carrying out investigations; analyzing and interpreting data, using mathematics and computational thinking; constructing explanations; engaging in argument from evidence; obtaining, evaluating, and communicating information) and the engineering design process (e.g., defining problems, iterative design, designing solutions) related to the characteristics of organisms and life processes, including safety procedures and the proper use of equipment.
Sample Item:
Students are using a light microscope to view a prepared slide of a cross section of the anther of a lily. Which of the following processes are they most likely to observe?
- Fertilization
- Diffusion
- Phagocytosis
- Meiosis
Correct Response and Explanation (Show Correct ResponseHide Correct Response)
D. Meiosis is a type of cell division used by sexually reproducing organisms. In the case of a lily, the anther is the male reproductive structure which produces pollen as the result of meiosis.
Descriptive Statements:
- Demonstrate knowledge of the historical evidence of the evolution of species over time (e.g., fossil records, homologies, DNA evidence, embryology).
- Apply knowledge of the principles of biological evolution (e.g., natural selection, gene flow, genetic drift), including how natural selection can lead to adaptation.
- Demonstrate knowledge of major events in the history of life, including mass extinctions and the evolution of organisms.
- Demonstrate knowledge of the diversity of life and the taxonomic relationships among living organisms.
- Apply the basic principles of heredity and genetics, including through Punnett squares and the laws of probability.
- Demonstrate knowledge of the nature of the genetic code and the basic processes of DNA replication and protein synthesis.
- Demonstrate knowledge of the causes and types of genetic and environmental mutations that occur in living organisms.
- Demonstrate knowledge of the methods and applications of genetic engineering.
- Demonstrate knowledge of scientific practices (e.g., asking questions; developing and using models; planning and carrying out investigations; analyzing and interpreting data, using mathematics and computational thinking; constructing explanations; engaging in argument from evidence; obtaining, evaluating, and communicating information) and the engineering design process (e.g., defining problems, iterative design, designing solutions) related to concepts and principles related to genetics and evolution, including safety procedures and the proper use of equipment.
Sample Item:
During a period of drought, the low level of water in a river makes it possible for squirrels of population A to migrate to a new region and mate with squirrels from population B. The resulting changes in allele frequency in population B are the result of which of the following mechanisms?
- natural selection
- gene flow
- mutation
- genetic drift
Correct Response and Explanation (Show Correct ResponseHide Correct Response)
B. Gene flow refers to the process by which alleles move between two populations of a species. In this example, the drop in water level allows breeding to occur between individuals from population A and population B, resulting in changes in allele frequency within population B.
Descriptive Statements:
- Demonstrate knowledge of the characteristics of terrestrial and aquatic biomes, including representative species of plants and animals that inhabit them.
- Apply knowledge of the interrelationships between producers, consumers, and decomposers in a variety of ecosystems and strategies used by different organisms to obtain the basic needs for life.
- Apply knowledge of the cycling of matter and the flow of energy through different types of ecosystems, including through food webs.
- Analyze the biotic and abiotic factors that affect population dynamics in ecosystems (e.g., competition, resource availability, habitat requirements).
- Demonstrate knowledge of factors that affect carrying capacities and biodiversity of ecosystems.
- Apply knowledge of the process of ecological succession and its relationship to stability and change.
- Demonstrate knowledge of scientific practices (e.g., asking questions; developing and using models; planning and carrying out investigations; analyzing and interpreting data, using mathematics and computational thinking; constructing explanations; engaging in argument from evidence; obtaining, evaluating, and communicating information) and the engineering design process (e.g., defining problems, iterative design, designing solutions) related to organisms, matter, and energy within ecosystems, including safety procedures and the proper use of equipment.
Sample Item:
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
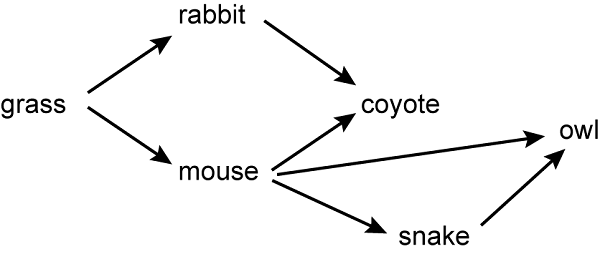
On the leftmost end of the diagram, grass has two arrows that lead to rabbit and mouse. The rabbit has one arrow that leads to coyote. The mouse has three arrows that lead to coyote, owl, and snake. The snake has one arrow that leads to owl.
In the food web shown, which of the following animals is a primary consumer?
- coyote
- grass
- rabbit
- snake
Correct Response and Explanation (Show Correct ResponseHide Correct Response)
C. Primary consumers rely almost exclusively on primary producers like plants to provide the calories they need to survive. In the food web shown, the rabbit feeds only on grass and would be considered a primary consumer.

